
2. Barbara has specific areas in her brain dedicated to speech, but they are separate from comprehension. She has a wider field of hearing and greater pitch detection. Kenneth does not have an area in his brain specifically dedicated to speech, has more restricted hearing which blocks out higher tonality and when he is concentrating on a task he is functionally deaf.
TIP 3: You may find women are more attentionally engaged, but check they understand the content even when they are nodding affirmation.
TIP 4: Get a male client’s attention before communicating, touch his shoulder or point to the notes.
Biochemistry: the blood
Beyond biology, men and women’s biochemistry differ remarkably. Barbara’s hormones (oestrogen and progesterone) change through her monthly cycle and her last pregnancy deeply affected her mood (she had post natal depression). Oestrogen acts as a neuro-stimulant and anti-depressant. Lack of it during menopause can cause angry outbursts and tearful regret afterward. Kenneth’s hormones (testosterone, MIS & DHEA) affect his concentration and heighten anger response in competitive situations.
TIP 5: Are you tuned in and sensitive to your female clients? Do you know what stage of life they are at? Separate genuine response from biochemical overreaction.
TIP 6: Young male clients whose blood is swimming with testosterone will find concentration for 60 minutes very difficult. Break up your session into three or four distinct parts or activities.
The neurology: the brain
In the womb a foetus is bathed in chemicals that deeply alter the brain’s structures. Louann Brizendine has published the results of her lifetime of research in “The Female Brain” and “The Male Brain” respectively. There is a spectrum from female gender, female brain (F-brain) through to male gender, male brain (M-brain). In between these two poles are women who have an M-brain and men who have an F-brain:
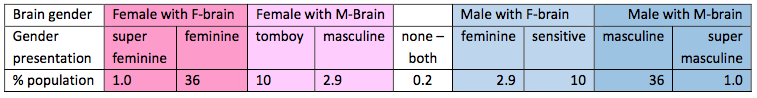
SIDENOTE: [Whilst coaching work is certainly done among Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual and Transgender populations – who almost certainly fall within the 6% in the middle of this table – very little research has been done on the brain differences of these groups.]
Barbara has an F-brain. She is very relationship oriented, group aware, emotionally intelligent, thinks of many things at once, looks for connections between things and does empathy well. Kenneth has an M-brain. He is very logical, goal directed, more single minded, defaults to taking action quickly, looks for outcomes and doesn’t do empathy well. There are at least five distinctions that affect our coaching with them:
1. Words
Barbara’s F-brain stores a dictionary of approximately 50,000 words and she employs an average of 7,500 words each day. She loves to process things verbally. Without a specific area for linguistics Kenneth’s M-brain is less inclined to keep an extensive vocabulary. He keeps a dictionary of about 35,000 words and uses just 3,000 words a day. Once they are used, he loses motivation to keep communicating.
Download Article 1K Club


















