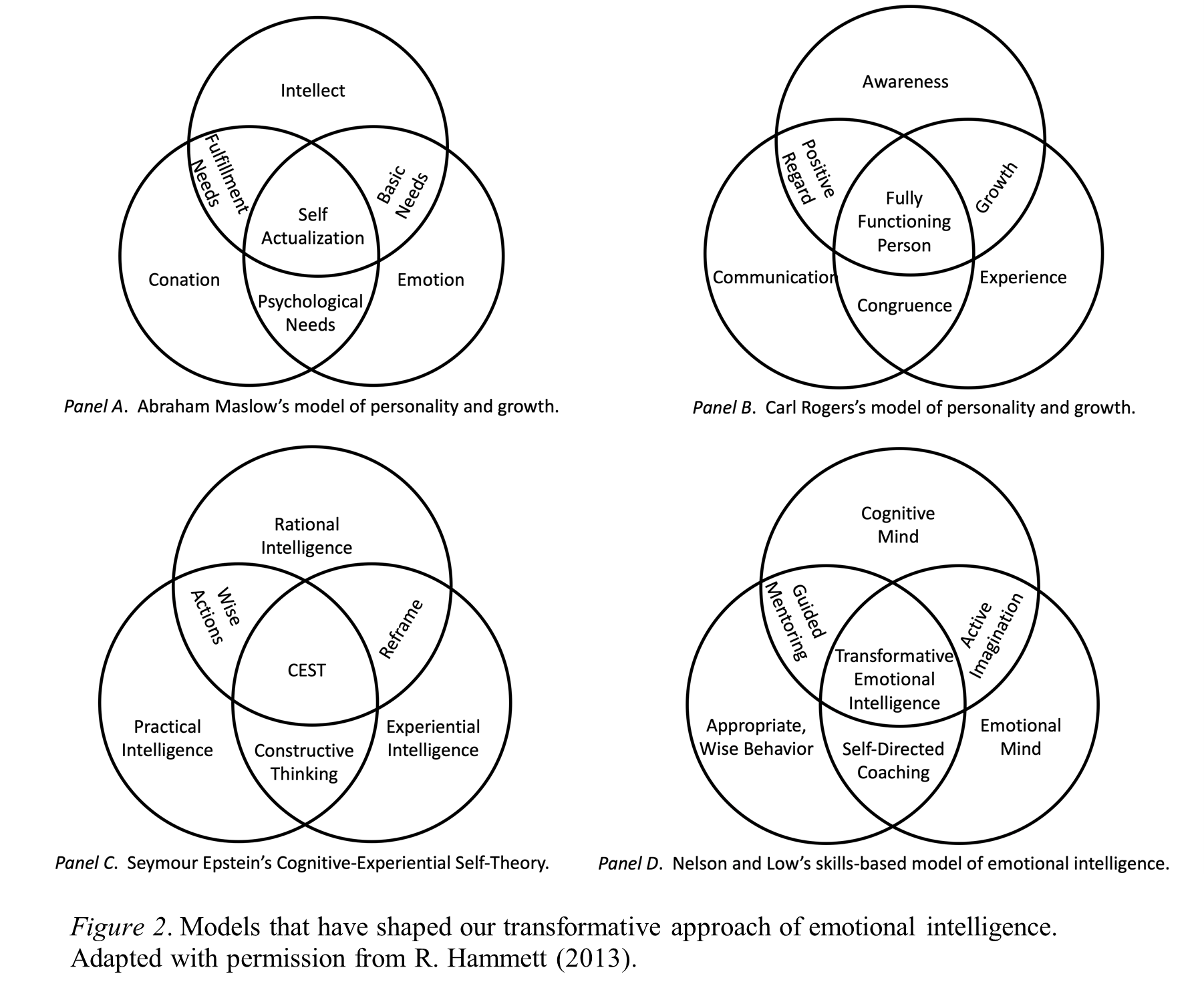
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs describes a process of growth and motivation that we view as important for relating the TEI principle of interdependence for developing healthy, productive relationships, key emotional-life skills, and constructive thinking. Our view of the relationship between Maslow’s hierarchy and our current views from research derived, person-centered, relationship-focused, and skills-based models of human behavior and life development are shared in Table 4. Note the PERL skills measured by SCALE® in the third column.
| Table 4. Work and Life Excellence: Needs, Beliefs, and EI Skills | ||
| Need Types | Related Beliefs | PERL Skills |
| Survival | Obtain pleasure and avoid pain in fulfilling physiological needs essential to life and well being | Anger Management, Anxiety Management, Stress Management, and Self Esteem |
| Safety | To make sense out of your experience and develop consistency and stability in how the world is viewed | Self Esteem, Stress Management, Positive Personal Change, Physical Wellness |
| Relationship | To seek meaningful connections and emotionally satisfying relationships with others | Assertion, Comfort, Empathy, Leadership, and Self Esteem |
| Self Esteem | To believe that one has value, worth, and dignity; to develop high self esteem | Self Esteem
|
| Equilibrium | To seek balance and harmony when we experience distress or perceive deficits | Anger Management, Anxiety Management, Stress Management, and Self Esteem |
| Growth | To commit to continuous growth and change as we seek to develop our best self | Self Esteem, Achievement Drive, Positive Personal Change, Physical Wellness |
| Note: Maslow’s (1954) contribution established a frame of reference for thinking about motivation that focuses on the subjective experience of the individual. Our connection, interpreted through related beliefs, emphasizes PERL skills that individuals can use to encounter, satisfy, and when necessary revisit needs in pursuit of personal growth. | ||